About the Project
In Nicaragua, the agriculture sector is the single largest employer with more than 30% of the labor force, the main source of livelihood for close to 80% of rural households, and the majority of staple foods consumed are derived from small- and medium-scale farmers. The Caribbean coast is the country’s main agricultural frontier, accounting for 43% of the national territory, 23% of the agricultural area, nearly three-quarters of the forest area, 70% of fishery production, and 35% of the cattle. However, agricultural growth is limited by post-harvest losses, weak agribusiness development services, lack of rural infrastructure, and climate change vulnerability.
PAIPSAN-CCN invested $33.9 million to focus on small producers, indigenous, afro-descendants, and mestizo communities, and value chains with growth potential in the impoverished Caribbean coast region of Nicaragua. The project enhanced food security and nutrition in select communities of Nicaragua’s Caribbean coast. The project targeted small- and medium-scale landholders, rural laborers, producers’ organizations, and fisher communities with limited or no assets or equipment, including women and young people, and aligned with the sector-wide Rural Development Program, which focused on poor smallholders as active participants in their own sustainable human development to achieve food security and foster agricultural exports. PAIPSAN-CCN promoted increased agricultural productivity and environmental sustainability through participatory design innovation development plans for formal and informal groups of beneficiaries, such as cooperatives and producers’ associations, to improve and innovate their products and consolidate market opportunities. Activities included agricultural technology training and technical assistance for organized producers and creating and promoting income-producing employment activities, such as family-community micro-enterprises ranging from cabinet-making and fruit production to sustainable tourism in support of women and young people. The project also supported nutrition education to change behavior and raises awareness and knowledge about nutrition and the role of agriculture in improving nutrition outcomes.
Country
- Nicaragua
Project Status
ClosedFunding
Country-led projectSupervising entity
- World Bank
Call Year
2013GAFSP Funding Amount
33.90Project Highlights
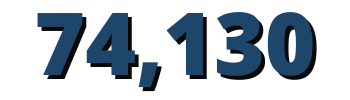
people benefited from the project, 47 percent were women
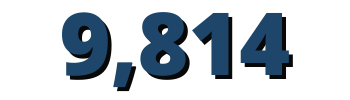
farmers have adopted project-promoted technologies, 4,751 were women
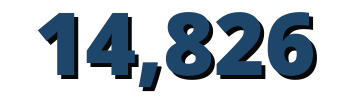
families implemented IDPs, 6,994 were women-led
Results
PAIPSAN-CCN benefitted 74,130 people (47 percent women), exceeding the end-of-project targets. As a result of project efforts, 9,814 farmers have adopted project-promoted technologies, of whom 4,751 were women, surpassing the end-of-project targets of 8,000 people and 1,600 women. In addition, 14,826 families (6,994 women-led) implemented IDPs, surpassing the end target of 14,000. The project financed 58 of these IDPs to improve agricultural production, small-scale fisheries, processing, value-addition, and commercialization. Surpassing the target of 2,000 beneficiaries, the project trained 10,692 people in nutrition education and the role of agriculture in improving family nutrition outcomes; among those trained, 5,682 were men, surpassing the end-of-project target of 800. Further, the average agricultural productivity increase reached 72 percent, far surpassing the 10 percent target, and the final Dietary Diversity Score was 91 percent, also surpassing the end-of-project target of 80 percent.
Contact
GAFSP Coordination Unit
gafsp-info@gafspfund.org
Documents
Official Project Documents:
